Awesome Animal Facts: Discover Nature's Wonders

Nature Topic Overview
Animal life on Earth is diverse and fascinating. This section open up the doors to that exploration, providing insight into remarkable traits exhibited by many species. Animals have peaked the curiosity of humankind with their alternatives, communicating their instincts and tastes through various means. As we dive into interesting animal facts, we cultivate intrigue among young minds while emphasizing the importance of the natural world surrounding them.
Being aware of animals helps raise awareness about biodiversity, habitats, and the enchanting way nature functions together. Through this exploration, the next generation will learn not only the beauty and complexity of animal species but also the subtle connections that bind every living organism.
Fun Facts and Trivia
Here are some eye-opening and captivating facts about amazing creatures:
- Axolotls can regenerate lost limbs.
- Crows can recognize human faces and even hold grudges.
- Dolphins have names they call each other.
- Octopuses have three hearts and can change their skin color for blending or signaling.
To engage young readers, consider interactive visuals like infographics or illustrations of various species. Visual aids encourage curiosity, creating vivid images of animals in readers' minds.
Did you know that hummingbirds are the only birds that can fly backward?
Wildlife Explorations
Explore various species adapted perfectly to their environments:
- Deserts: The Fennec Fox uses its large ears to disperse heat.
- Rainforests: The Arctic Tern has the longest migration route among birds, spanning up to 44,000 miles.
- Oceans: The Blue Whale is the largest known animal to ever exist.
When detailing facts about each species, include clues to environmental interactions, added marvels of survival showcased in particular habitats, and essence of ecosystems that encapsulate thriving life.
Encouraging quizzes also helps in retaining information. Challenge your young learners by asking,
Preface to Animal Facts
Understanding the intricate world of animals is crucial. Each species comes with its unique set of features and roles within ecosystems. Knowing animal facts allows us to appreciate biodiversity and recognizes the interconnectedness of life. This introduction serves as a gateway to learn more about the animal kingdom.
Why Animal Facts Matter
Animal facts matter for several reasons. Firstly, they allow us to discover the extraordinary adaptations that various species have developed over time. These adaptations are fascinating and often surprising. For example, did you know that the heart of a blue whale is as large as a small car? Another essential point is the contribution of animals to our ecosystems. Every creature plays a role. From pollinators like bees to predators like wolves, the balance of nature relies on these relationships.
Animals also play a significant roles in human culture and history. By learning about different species, we foster a connection between humans and the natural world. This connection helps promote empathy toward animals, encouraging conservation efforts. However, understanding their behaviors and needs is vital to coexistence. When people know more about animals, they can make educated choices to protect their habitats and futures.
The Importance of Animal Education
Animal education offers approaches to instill knowledge about the world around us. Educating children about animals is particularly beneficial. It supports curiosity about nature and the environment. Consider when children learn about animal behaviors or diets. This not only informs them but also empowers them to expand their perspectives.
Two crucial aspects of animal education include:
- Promoting an inquiry-based learning process. This encourages children to ask questions, seek information, and explore further.
- Facilitating experiences through observation. Sightings of wild animals create memorable moments that inspire young learners.
Furthermore, understanding animal facts can lead to informed discussions surrounding conservation. Educating both children and adults leads to actionable steps taken toward preserving wildlife.
Mammals: The Diverse Group
Mammals hold a unique position in the animal kingdom. They are warm-blooded vertebrates characterized by features such as hair or fur, mammary glands, and specialized teeth. This section explores the diverse group of mammals, showcasing their significant role in ecosystems and highlighting the remarkable adaptations that enable them to thrive in various habitats. Understanding mammals enriches our appreciation of nature and emphasizes the need for empathy in conservation efforts.
Unique Features of Mammals
Mammals share certain distinctive features that set them apart from other animal groups. One prominent feature is their ability to regulate body temperature internally, referred to as warm-bloodedness. This allows them to survive in a range of environments, from tropical jungles to frozen tundras.
Mammal anatomy includes:
- Hair or fur: Provides insulation and protects the skin.
- Mammary glands: Enable females to nurse their young with nutrient-rich milk.
- Specialized Teeth: Adapted for various diets, supporting their roles as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores.
With over 5,000 species, mammals range from the tiny bumblebee bat, which weighs less than a penny, to the enormous blue whale, the largest animal on Earth. Their diversity illustrates the adaptability and resilience of this group in the face of environmental changes.
Fascinating Mammal Adaptations
Mammals have developed a wide array of adaptations that make them suited to their habitats. Some mammals, like the Arctic fox, have thick fur to withstand cold temperatures, while others, like the kangaroo, possess strong hind legs for hopping across vast distances.
Fascinating adaptations include:
- Echolocation: Bats and some whales use sound waves to navigate and locate prey.
- Camouflage: Many species, such as the snow leopard, have markings that help them blend into their surroundings, enhancing hunting success and avoiding predators.
- Extreme Longevity: Some mammals, like the bowhead whale, can live over 200 years.


These adaptations not only ensure their survival but also reflect the intricate relationships mammals have with their environments and each other.
The World of Marine Mammals
Marine mammals, such as dolphins, whales, and seals, inhabit our oceans, presenting unique adaptations for life in water. Unlike terrestrial mammals, they are specially suited to an aquatic lifestyle.
Key features of marine mammals include:
- Streamlined bodies: Allow efficient movement through water.
- Blowholes: Facilitate breathing at the surface without fully emerging.
- Social Structures: Many species, such as dolphins, exhibit complex social behaviors, fostering bonds within pods.
The vocal sounds of marine mammals are remarkable. For example, humpback whales compose intricate songs that can travel extensive distances underwater.
Understanding marine mammals is crucial not only for biodiversity but also for considering how human activities impact their existence. With climate change and ocean pollution, learning about these creatures fosters a sense of responsibility towards preserving their habitats.
Birds: Masters of Flight
Birds are truly remarkable creatures. Their ability to fly allows them to reach parts of the world that many other animals cannot. This unique skill of flight aids in their survival. They can escape predators and find food easily. Understanding birds, their anatomy, and behavior helps us appreciate our environment better. Knowledge about birds also encourages interest in wildlife conservation efforts.
The Anatomy of Birds
The bodies of birds are fascinating. They have adaptations that make flying easier. For example:
- Hollow Bones: While they need a sturdy skeleton, through evolution, birds developed bones that are lighter and stronger. This allows for graceful flights without added weight.
- Feathers: Feathers serve many purposes, including insulation, waterproofing, and of course, enabling flight. The various types of feathers provide adaptability in different environments.
- Specialized Muscles: Birds have strong breast muscles that power their wings. These muscles help birds flap quickly and fly long distances.
Given these structures, you can see how their bodies are suited to life in the skies.
Unusual Bird Behaviors
Birds exhibit behaviors that are sometimes strange yet practical for survival.
- Tool Use: Some bird species, like the New Caledonian crow, are known to use tools to obtain food. They take sticks or leaves to extract insects from tree bark.
- Dancing and Vocalizations: Male birds often perform elaborate dances or unique calls to attract females. These displays are not merely for show, they also indicate good health.
- Playing: Certain bird species, such as parrots, have been observed engaging in play. This helps develop social bonds and learn important life skills.
These behaviors emphasize the complex lives of birds and their interactions with each other and their environment.
Migration: An Impressive Journey
Many bird species travel long distances each year, a process called migration. Migration is a crowded and seasonal phenomenon. Here are some reasons why birds migrate:
- Weather: In the winter, some regions may become too cold and food scarce. Birds travel south to find warmer climates and abundance of food.
- Reproduction: Even in spring, certain species move to breeding grounds to find mates. Warmer conditions are ideal for raising chicks successfully.
- Natural Instinct: Migration is often instinctual. Birds often follow set patterns year after year.
Migration routes can be thousands of miles. Certain species, like the Arctic Tern, travel from the Arctic to the Antarctic. This journey is one of nature’s most impressive feats.
Understanding bird migration is crucial to conserving their habitats and ensuring their survival for future generations.
Reptiles: Ancient Survivors
Reptiles represent one of the oldest branches of life, and their adaptations reflect an enduring legacy within the animal kingdom. These creatures have survived significant changes on Earth, from mass extinctions to drastic shifts in climate. Understanding reptiles is key to many aspects of biology and conservation. Studying them allows us to appreciate nature’s resilience and adaptability.
When we delve into their characteristics, we reveal their bodily designs and survival strategies through the ages. Misconceptions about reptiles often partake in many narratives about their nature. Instead, highlighting their versatility helps challenge fears and biases.
We also see how various defenses, such as camouflage, help reptiles thrive. Their evolution often includes methods that let them blend into their surroundings, forming essential parts of their survival techniques. Such aspects help engage young readers and motivate them to learn further about these intriguing creatures.
Reptilian Characteristics
Reptiles have distinct features that differentiate them from other animal types. These traits include:
- Cold-blooded: Unlike mammals, reptiles cannot regulate their body temperature internally. They rely on external sources like sunlight or shade to keep warm or cool.
- Scaled Skin: Their skin is covered in scales made of keratin, which prevents water loss. This is crucial for survival in diverse environments, particularly desert ecosystems.
- Lung-based Respiration: All reptiles breathe using lungs. This trait is imperative since it defines their need for air regardless of the environment.
- Egg-laying: Most reptiles lay eggs, although some give birth to live young. Their eggs often have a leathery shell, aiding in moisture retention in different environments.
Understanding these characteristics lets educators relay the complexities of reptiles in a child-friendly way, tugging at curiosities of younger audiences. It demonstrates not only their evolution but effective arts of survival in changing environments.
Camouflage and Defense Mechanisms
In the world of reptiles, camouflage serves as a vital defense mechanism. It allows many species to avoid predators and become effective hunters themselves.
- For instance, a chameleon can change its skin color to blend in with its surroundings. This not only keeps it safe but also aids in hunting insects. Their ability to manipulate colors is complex, Angular reflections from light allow adaptability.
- Another example is the horned lizard that can flatten its body, merging seamlessly into its surroundings among rocks. With its spiny defense mechanisms, it provides an extra layer against predators.
Reptiles also use behaviors like remaining still or mimicking their environment. Mystery surrounds many in the animal kingdom, and appreciating these features informs conversations on respecting living beings. Through discussing camouflage, an awareness of the delicate balance of ecosystems emerges in young minds.
“Reptiles use various strategies to evade detection; understanding these abilities contributes significantly to wildlife conservation.”
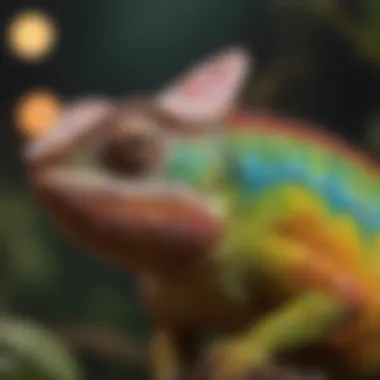

Therefore, impressing the younger audience through educative discussions of traits, camouflage, and evolutionary templates lures them into the beautiful complexities of reptiles held in the natural world.
Amphibians: Dual Lives
Amphibians are a fascinating group of animals, embodying a unique way of life that greatly benefits the ecosystems they inhabit. Being able to live both in water and on land sets them apart from many other animals. This dual lifestyle influences everything from their reproductive strategies to their evolutionary adaptations. Understanding amphibians helps us to learn about the health of our environment, as they often act as indicators of ecological quality. Their existence and thriving populations reflect the complex balance between aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
The Life Cycle of Amphibians
Amphibians undergo a remarkable transformation during their life cycle, known as metamorphosis. Starting as eggs, they usually hatch into larval forms such as tadpoles in many species. These tadpoles live in water and breathe through gills. Gradually, they develop legs, lungs, and eventually lose their tails, transforming into the adult form. This gives them the ability to venture onto land.
The process can vary among different species of amphibians. Here are key points about their life cycle:
- Eggs: Most amphibians lay eggs in water. These eggs are soft and gelatinous, allowing larval stages to grow in a safe, aquatic environment.
- Tadpoles: After hatching, tadpoles primarily consume plant matter. Their rapid growth is essential for survival in water before they shift to a terrestrial habitat.
- Metamorphosis: This crucial stage involves significant changes. Limbs develop, gills are replaced by lungs, and diets shift to include insects and other small organisms.
- Adults: Once they reach adulthood, many amphibians are adapted for life on land but often return to water to reproduce. This cycle allows for adaptation to different habitats extensively.
The ability to move between water and land is a vital aspect of their lifecycle. It showcases a successful adaptation that links both environments while providing multiple opportunities for survival and reproduction.
Unique Habitats of Amphibians
Amphibians inhabit a diverse range of environments. They are commonly found in wetlands, such as ponds, marshes, and swamps. However, some species adapt to unique conditions. Here are some observations about their diverse habitats:
- Wetlands: These are ideal for many amphibians. They provide breeding grounds where eggs can be protected from predators while serving as suitable habitats for young tadpoles.
- Forests: Some amphibians prefer humid forest environments, where they can find sufficient cover and plenty of insects.
- Deserts: Interestingly, certain amphibians can survive in arid regions by burrowing into the ground. They enter a state of dormancy until moisture returns.
- Grasslands: Amphibians can be found in grasslands, especially during the wet season when shallow pools form. This provides a temporary habitat for breeding.
These diverse habitats highlight the adaptability of amphibians. Being able to thrive in various environments allows them to play critical ecological roles, such as controlling insect populations and serving as food sources for other species.
This ability to inhabit both water and land, along with their sensitive nature, underscores the relationship amphibians have with the environment. Protecting your habitats is essential for their survival and the entire ecosystem's health.
Fish: Gills and Fins
Fish are remarkable creatures that inhabit a variety of water environments in our planet. They adapt well to both freshwater and saltwater ecosystems. Gills and fins are two essential features that allow fishes to thrive underwater efficiently. Understanding these elements is critical not just for admiring their beauty, but also for grasping the roles which fish play in the broader ecosystem.
Types of Fish: A Variety of Species
There are thousands of species of fish in the world, each with unique characteristics. Some primary categories include:
- ** bony fish:** They make up about 95% of all fish species. Examples are salmon and trout. Their bodies have bones instead of cartilage.
- ** cartilaginous fish:** Sharks and rays fall under this group. They have skeletons made of cartilage rather than bones.
- ** jawless fish:** Ancient in lineage, jawless fish like lampreys and hagfish show a very simple structure. Typically, they feed in unique ways, like sucking nutrients from other fish.
Every type of fish fulfills specific ecological niches. For example, predators like the great white shark maintain balance in marine populations by controlling species numbers.
The Role of Fish in Ecosystems
Fish are crucial for ensuring healthy aquatic ecosystems. Here are some dynamic contributions of fish in nature:
- Cycle of nutrients: Fish help recycle nutrients through different levels of the food chain. By consuming algae and small organisms, they allow for a balanced ecosystem, fostering overall health.
- Habitat structure: Some fish, such as parrotfish, aid in creating healthier coral by grazing on harmful algae. This leads to healthier reefs, which support numerous marine life forms.
- Food source: Fish serve as food for various other creatures, including birds, marine mammals, and even humans. The food web is complex, relying on fish for stability.
Fish are fundamental to both marine biodiversity and economic prosperity for many coastal communities worldwide.
Understanding fish diversity and their roles provides insights into the ecosystem's delicate balance. Ignoring these organisms risks destabilizing the natural world. By learning about fish, readers can appreciate their importance to aquatic ecosystems and, consequently, to humanity.
Insects: The Most Abundant
Insects represent one of the most versatile and diverse groups in the animal kingdom. Their impact stretches across ecosystems and life forms. Understanding insects is crucial for appreciating nature’s balance. As we explore this section, we will cover their anatomy and classifications, and the significant effects they have on the environment.
Insect Anatomy and Classifications
Insects are characterized by a unique body structure. Most have three main parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. The head contains sensory organs like the antennae and compound eyes. Their thorax is where legs and wings attach, giving them mobility in various environments. Finally, the abdomen houses important organs such as the digestion system.
In terms of classification, insects fall into several orders. Common examples include:
- Hymenoptera: Bees and ants fall into this group, known for their complex social structures.
- Coleoptera: This order includes beetles, possessing a hard exoskeleton called an elytra.
- Lepidoptera: Butterflies and moths are well-known for their colorful wings.
Insects undergo different life cycles, including distinct stages such as egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage serves a vital role in their development.
While there are millions of insect species identified and potentially many more yet to be discovered, they act as pollinators, food sources, and decomposers, proving vital to the rhythms of ecosystem health. Understanding their anatomy and life cycle lays the foundation for recognizing their ecological roles.
Impact of Insects on Nature
Insects play multifaceted roles in nature, made visible through their interactions with other species and their environments. They serve as crucial pollinators for countless plants. Approximately one-third of the food we consume relies on the pivotal service of insect pollinators. These insects transfer pollen from flower to flower, assisting with plant reproduction.


Additionally, insects provide vital functions such as:
- Nutrient cycling: Insects aid in breaking down organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil.
- Food source: Many creatures, including birds and mammals, depend on insects as their primary food source.
While insects have remarkable benefits to nature, they also face threats postulated due to habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change. The decline of insect populations indicates broader environmental issues and necessitates immediate attention. Greater awareness and understanding of insects empower informed decisions about how individuals can impact their survival.
Insects may be small, but their contributions to ecosystems are monumental. Each species plays a role, often unseen but essential for sustainability.
Encouraging kids to explore the world of insects fosters greater appreciation for biodiversity and its thriving complexities. Knowing more about these abundant creatures offers insights into maintaining ecosystem health and definitive reminders of interconnected lives.
Conservation: Protecting Animal Life
Conservation is vital for maintaining biodiversity across our planet. In this section, we will examine why the protection of animal life is so important, looking at specific threats that many species currently jagged and the enthusiastic efforts being implemented, both locally and globally, to combat these issues. Protecting animals and their habitats is not just crucial for their future; it ensures the health of our entire planet. Healthy ecosystems contribute diverse resources and elements essential for life. Hence, understanding our role in conservation influences not only the animals we cherish but also our collective future.
Threats to Animal Species
Many animal species are currently facing numerous threats. Recognizing these perils is the first step towards creating solutions. Some of the main threats include:
- Habitat Loss: Due to urbanization, agriculture, and logging, many animals find their homes vanishing. This leads to overheured depletion and a decrease in populations.
- Climate Change: Changes in climate affect migration patterns, breeding seasons, and food availability. Warming temperatures impact polar bears, coral reefs, and many more species.
- Pollution: Contaminants in air, water, and soil damage animal habitats and endanger their life. Plastic waste is frequently ingested by marine life, leading to severe health issues.
- Overfishing and Hunting: Excessive harvesting of species can create an unbalancing problem in oceans and forests, making it difficult for them to recover.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can disturb local ecosystems, outcompeting, predating, or bringing diseases to native species.
It is essential for us to recognize these threats to advocate for the safeguarding of animal life. This advocacy can help foster healthy ecosystems while ensuring the survival of various species.
Conservation Efforts Worldwide
Across the globe, committed individuals and organizations work tirelessly to combat threats to animal life. The following are notable conservation efforts that have been made:
- Protected Areas: National parks and wildlife reserves were created to offer safe havens for many endangered species. They encourage biodiversity by prohibiting significant human interference.
- Wildlife Corridors: These pathways help animals migrate safely between habitats, prompting genetic diversity.
- Restoration Projects: Many organizations focus on not only preserving current habitats but also restoring damaged ecosystems. This involves reforesting areas or removing damaging infrastructure.
- Legislative Efforts: Laws such as the Endangered Species Act in the United States provide necessary legal protection for threatened and endangered species. These means stop poaching and habitat declines.
- Community Involvement: Local communities are often at the heart of effective conservation. Empowering locals helps to ensure the sustainable use of resources while protecting essential habitats.
Engagement with science and local culture enables productive conservation strategies.
Through these means, the conservation initiatives showcase tremendous importance specifically attending to the well-being of animal species while attempting to propagate cultural appreciation of nature's intrinsic value. We can foster a healthier future for animal life and our environment if we collectively understand their roles and challenges. Such initiatives are essential for educating the younger generation, making them ally necessary efforts early on, leading to a fruitful collaboration toward a sustainable future.
Engaging with Nature
Engaging with nature is a critical aspect of understanding and protecting the intricate web of life that surrounds us. For children and adults alike, it serves two pivotal roles: enhancing knowledge about planetary biodiversity and fostering a sense of responsibility towards that biodiversity. Through direct interaction or observation, the wonders of animal behavior and unique habitats become more than abstract concepts. They evolve into opportunities for personal exploration and education. Nature is an endless classroom, full of lessons waiting to impart knowledge. Personalized experiences in natural settings inspire curiosity and a lifelong passion for wildlife.
Ways to Explore Animal Habitats
Exploring animal habitats can be both enjoyable and educational. Here are some effective ways to delve into the diverse worlds where animals live:
- Visit Local Parks or Nature Reserves: Observing animals in their natural surroundings can be enlightening. Nature walks provide views of various species while introducing the flora around them.
- Conduct Neighborhood Wildlife Surveys: Watching for local wildlife outdoors not just at parks but right outside the house promotes active engagement. It could mean counting birds or simply gazing at the insects inhabiting gardens.
- Search for Educational Programs: Many organizations offer field trips, guided nature walks, or workshops, specifically aimed at exploring wildlife habitats.
- Utilize Online Resources: Numerous websites, such as Wikipedia, have valuable information on different species and their habitats. Watching documentaries can also provide extensive understanding of wildlife.
By adopting these approaches, individuals, especially young learners, foster an innate appreciation for various ecosystems while gaining first-hand experience regarding the importance of habitats.
How to Encourage Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife conservation requires collective effort and dedication. Here are ways to encourage this critical cause:
- Educating Others: Share interesting animal facts and knowledge about ecosystems with peers. Young people can create presentations or organize discussions within their schools or communities.
- Participating in Local Conservation Programs: Getting involved with campaigns aimed at protecting habitats or specific endangered species can be enlightening and impactful.
- Promoting Responsible Use of Resources: Teaching young individuals about sustainable practices could lead to more conscientious consumers. This includes reducing plastic usage, recycling, and supporting local wildlife.
- Engaging on Social Media: Sharing and following conservation causes on platforms like Facebook and Reddit raises awareness and highlights ongoing efforts among a broader audience.
Taking these actions cultivates a culture of compassion towards nature, ensuring its sustainability for generations to come. Protecting wildlife and encouraging conservation fosters respect for the environment and lays the foundation for an ecosystem that flourishes.
“The future of our planet lies in the actions we take today concerning our wildlife and habitats.”
Closure: The Importance of Knowing Animals
Understanding animals is crucial to fostering a profound relationship with our environment. This article highlights various features and behaviors displayed by different species. Propagating knowledge about animals does not only serve an entertaining purpose; it cultivates empathy and responsibility among young people towards the natural world. When children understand animal behaviors, they learn to appreciate every click, whistle, and roar of the creatures around them.
As future caretakers of the Earth, this knowledge benefits not just individuals, but entire communities and ecosystems. It emphasizes interconnectedness, making kids realize that their actions have consequences on animal lives and habitats. While aiming for a practical approach, it teaches principles of biodiversity, food chains, and ecology in a simple manner. This engagement with wildlife shapes childnes minds and prepares them for bigger responsibilities as adults.
“But friends are the famaily we choose.” - Everybody loves their family this way! A cultivated love for nature encourages one to seek futher imformation and explore beyond known.
Animal Knowledge and Future Generations
Teaching children about animals builds a foundation of ecological literacy. Engaging with nature from an early age helps them to understand various animal species and their unique needs. As they evolve, so does their understanding of how animals like tigers, dolphins, and penguins lead their lives. Consequently, they grow into informed advocates for wildlife.
This knowledge ensures a cycle of respect.Adult individuals carry forward what they learn. Emerging issues like habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change can only be effectively addressed if young people understand the impact of these activities on animals. Greater comprehension leads to clarity of thought and responsibility towards all living beings. As children educate others, they contribute meaningfully to the broader discussions of conservation and animal rights.
Inspiring a Love for Nature
A holistic understanding of animals paves a way for genuine emotional connections towards the environment. Knowing how a meerkat sends warnings to its group or why a monarch butterfly migrates provides young minds a context that fosters admiration. This grasp encourages appreciation for nature's artistry and complexity.
By showing the links between human actions and wildlife well-being, children feel driven to make an impact. Simple local initiatives, such as backyard bird watching, school garden projects, or park cleanups can stir engagement. They become little champions advocating for animal rights and restoration projects.
Thus, nurturing an exhaustive base of animal knowledge results in more celebrations of life sciences. Children leave school with an awareness of species, natural habitats, and everyone’s essential presence in the cycle of life, insuring that coming generations embrace the majestic world we are stewards of.







