Discovering Guatemala: Insights and Unique Facts
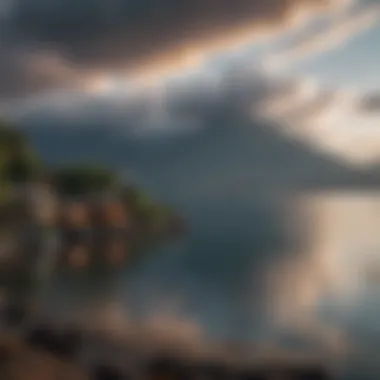

Nature Topic Overview
Guatemala is a hidden gem in Central America. Rich in culture and natural beauty, this country offers much more than just picturesque landscapes. It is surrounded by volcanoes, mountains, and the Caribbean Sea. The biodiversity found in Guatemala is staggering, with many species of plants and animals not seen anywhere else. Understanding this country invites one to discover its ecological complexity and cultural depth. In this article, we will explore various aspects of Guatemala, from its unique geography to its vibrant cultural heritage.
Fun Facts and Trivia
Here are some interesting facts to pique the curiosity of young readers:
- Volcanoes: Guatemala is home to 37 volcanoes. Some are still active, like Fuego, which constantly reminds people of nature's power.
- Mayan Heritage: The ancient Mayan civilization thrived here. Their impressive ruins, like Tikal, inspire awe and curiosity.
- Biodiversity: More than 700 species of birds make their home in Guatemala, making it a birdwatcher's paradise.
The colorful and interactive nature of these facts can be enhanced with visuals, such as maps and images, to make learning fun and engaging.
Wildlife Explorations
Guatemala's unique ecosystems host a variety of wildlife. Here are a few notable species:
- Quetzal: This bird is the national symbol of Guatemala. Its stunning colors make it a favorite among birdwatchers.
- Jaguar: They inhabit Belize and Guatemala, playing a vital role in their natural habitat.
- Ceiba Tree: Known for its long trunk and broad canopy, it holds cultural significance among the Maya as a sacred tree.
Children can participate in wildlife quizzes to learn more about these species and their habitats, expanding their understanding of nature's wonders.
Environmental Awareness
The conservation of Guatemala's natural resources is crucial. Deforestation and climate change impact wildlife and ecosystems greatly.
To protect this unique environment, children can:
- Plant trees to combat pollution.
- Participate in local clean-up events.
- Learn about and support sustainability efforts.
Understanding the importance of conservation will help young minds become stewards of the environment.
DIY Nature Activities
Hands-on learning can be incredibly rewarding. Here are a few projects kids can try at home:
- Nature Journal: Encourage kids to keep a journal of their outdoor explorations. They can document plants and animals they see.
- Crafts: Use leaves and twigs to make art and crafts, promoting creativity while celebrating nature.
- Field Guide Creation: Help children create a simple field guide. They can Illustrate local plants and animals, fostering curiosity and learning.
These activities not only make learning enjoyable but also encourage observations about nature, strengthening the bond with the environment.
Geographical Overview of Guatemala
Understanding the geographical overview of Guatemala is key for grasping the essence of its identity. The landscape of Guatemala shapes its culture, history, and even its economy. This section will explore the location, borders, and the rich geographic features that define this Central American nation. By recognizing the unique aspects of Guatemala’s geography, we can appreciate the factors that make it an intriguing place to visit and learn about.
Location and Borders
Guatemala is located in the heart of Central America, bordered by Mexico to the north and west, Belize to the northeast, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast. Its strategic location allows for a blend of diverse cultures and influences. Guatemala occupies a small area of about 108,889 square kilometers, yet it is densely packed with natural wonders and historical significance. This proximity to the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean also plays a role in its climate and trade opportunities. The presence of multiple borders not just enriches its culture, but allows easier access for both tourism and commerce, connecting Guatemala with its neighbors.
Major Geographic Features
Volcanic Mountains
Guatemala is famous for its volcanic mountains, with more than 30 volcanoes scattered across the country. This mountainous landscape plays a vital role in shaping the ecology and economy of the region. The key characteristic of these volcanoes is their active status, including notable ones like Volcán de Fuego and Volcán de Agua. These active volcanoes offer both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, they present risks of eruptions. On the other hand, they contribute to the rich soil fertility, supporting agriculture. The mountainous terrain is a beneficial choice for those studying geology and volcanology, as it provides real-world examples of tectonic activity and volcanic phenomena. Additionally, the scenic beauty attracts ecotourism.
Lakes and Rivers
Lakes and rivers are another significant aspect of Guatemala's geography. The country is home to beautiful lakes like Lake Atitlán and numerous rivers, including the Usumacinta. The key characteristic of these bodies of water is their ecological importance. They serve as habitats for various wildlife, including fish and birds, supporting biodiversity. These lakes and rivers not only enhance the natural beauty but also contribute to recreation and tourism. Visitors can engage in activities like kayaking and fishing. The unique feature of the lakes, particularly Lake Atitlán, is its stunning scenic backdrop of volcanoes and rich Mayan culture surrounding it, making it a popular choice for travelers.
Climate Diversity
Guatemala exhibits remarkable climate diversity, which is another fundamental aspect of its geography. The different climatic zones contribute to the variety of flora, fauna, and agricultural products available.
Tropical Regions
The tropical regions of Guatemala are primarily found in the lowland areas. The key characteristic of these regions is their warm temperatures and high humidity. This climate is significant for growing tropical crops like coffee and bananas, contributing to the country’s economy. The lush landscapes found in these parts support vibrant ecosystems. However, this climate also has disadvantages, such as the risk of hurricanes during the rainy season, which can affect livelihoods. Despite these challenges, the tropical regions are a beneficial choice for studying tropical biodiversity.
Cool Highlands


In contrast, the cool highlands of Guatemala offer a different climate. This area has cooler temperatures due to higher altitudes. The key characteristic of these highlands is the production of valuable crops like corn and vegetables. The scenic views in the cool highlands draw visitors and are a central part of the indigenous culture. The unique feature of this region is its diverse microclimates, again emphasizing its agricultural significance. These highlands provide a benefit for those exploring indigenous traditions and agricultural practices.
"The geographical wonders of Guatemala not only enhance its aesthetic appeal but also play a crucial role in its cultural and economic identity."
Overall, the geographical overview lays a firm foundation for exploring Guatemala further. It sets the stage for understanding the nation's rich history, vibrant culture, and extensive biodiversity.
Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of Guatemala is vital for appreciating its rich cultural heritage and complex societal structures. This section will explore the significance of ancient civilizations and colonial history, underscoring how these elements shaped modern Guatemala. Knowledge of the past not only helps in understanding present-day challenges but also highlights the resilience and adaptability of its people.
Ancient Civilizations
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization is one of the most significant aspects of Guatemala's history. Flourishing from around 2000 BC to 1500 AD, it is known for its incredible achievements in areas such as mathematics, astronomy, and architecture. The Mayans created impressive cities like Tikal and Quiriguá, which still hold archaeological value today.
A key characteristic of the Maya civilization is its complex social structure. It had a hierarchy that included kings, priests, and commoners. This structure is a beneficial aspect of the article as it gives insight into how social dynamics functioned in ancient societies.
A unique feature of Maya civilization is their writing system, one of the most sophisticated in pre-Columbian Americas. It allowed them to record their history and religious rituals, providing valuable information for today’s scholars studying Mesoamerican history. However, a disadvantage in our current understanding of Maya civilization is the loss of many texts and records over time, which makes complete reconstruction difficult.
Archaeological Sites
Archaeological sites are critical for uncovering the past. In Guatemala, sites such as Tikal and Yaxhá offer glimpses into the lives of the Maya. These locations provide evidence of monumental architecture, pottery, and tools, marking the technological advancements of that time.
The key characteristic of these archaeological sites is their ability to attract researchers and tourists alike. This is a beneficial element in appreciating Guatemala's rich past. Visitors experience firsthand the grandeur of Mayan architecture, sparking interest and awareness of historical preservation.
A unique feature of these sites is their UNESCO World Heritage status. This recognition helps in the conservation and study of these locations, although it also brings challenges, such as balancing tourism with preservation efforts. The pressures of tourism can impact site integrity, making careful management crucial.
Colonial History
Spanish Conquest
The Spanish conquest in the 16th century drastically transformed Guatemala. Following the arrival of Hernán Cortés and other Spanish explorers, the region experienced significant cultural and political upheaval. The conquest marked the beginning of colonial rule, which disrupted existing systems and imposed new governance.
A key characteristic of the Spanish conquest is the introduction of Catholicism. This had lasting effects on Guatemalan culture and social structures, providing a religious framework that persists today. Discussing this conquest is beneficial, as it helps understand the roots of current religious practices and community values.
A unique feature of the Spanish conquest is the amalgamation of cultures. Spanish influence intermingled with indigenous traditions, creating a unique cultural blend. However, this blend also contributed to the erasure of some indigenous practices and languages, a drawback that many communities still strive to revitalize.
Impact on Indigenous Peoples
The impact of the Spanish conquest on indigenous peoples is profound and multifaceted. The introduction of new governance systems, different economic practices, and foreign diseases led to drastic population declines and loss of traditional lifestyles.
A key characteristic of this impact is the social stratification that arose. It placed indigenous peoples at the bottom of the social hierarchy, affecting their rights and access to resources, which is a significant aspect of the article.
Discussing this impact is beneficial as it underscores ongoing struggles for rights, recognition, and cultural preservation. The fallout from colonization shapes contemporary movements advocating for indigenous rights.
A unique feature of the interaction between indigenous communities and the Spanish is the resilience of indigenous cultures. Despite centuries of colonization, many communities have preserved their languages and traditions. However, ongoing struggles against assimilation continue to pose challenges for cultural survival.
Understanding the historical context of Guatemala reveals a layered narrative of both resilience and adaptation, since ancient civilizations to colonial influences.
Cultural Richness
Cultural richness defines the spirit of Guatemala, showcasing its complex history and diverse traditions. This section explores the elements that contribute to this vibrancy. By understanding cultural richness, we can appreciate how different influences shape the identity of the country. Each aspect discussed reveals insights about daily life, customs, and collective memory of the Guatemalan people.
Multicultural Society
A multicultural society is fundamental to Guatemala. The blend of various ethnic groups creates a unique social fabric.
Indigenous Peoples
Indigenous peoples stand as a key component of Guatemala's identity. They represent the heritage of the ancient Maya civilization. Their language and customs form a vital part of modern Guatemalan culture. Each community maintains its distinctness, adding to the country's diversity.
Their traditional practices such as weaving and agricultural methods are not only artful but also practical. These traditions offer a connection to the past, allowing the younger generation to learn valuable skills. However, challenges exist. Many indigenous communities face economic and social issues that affect their quality of life. Highlighting their role in culture is crucial.
Spanish Influence
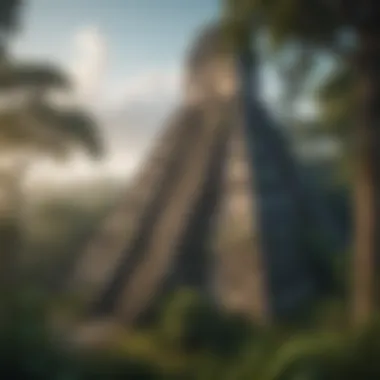

Spanish influence is another significant factor in Guatemala's cultural narrative. Since the Spanish conquest, many aspects of Spanish culture integrated into local traditions. This influence is visible in language, religion, and architecture. Spanish is the official language and is widely spoken across the country.
The merging of indigenous and Spanish customs creates a unique environment for communities. For example, religious festivals often blend Catholic and indigenous beliefs. However, a drawback of this influence is the risk of overshadowing indigenous identity. Balancing these cultures is vital for a true representation of Guatemalan society.
Traditional Festivals
Traditional festivals in Guatemala reflect the richness of its culture. These events provide insight into community traditions and values, drawing participation from diverse groups.
Semana Santa
Semana Santa or Holy Week is a prominent celebration noted for its elaborate processions and artistry. This festival takes place during the week leading up to Easter. Its key characteristic is the colorful alfombras or carpets made from dyed sawdust and flowers. These artworks align with processions that honor the passion of Christ.
This festival not only strengthens community bonds but also attracts tourists eager to experience its unique beauty. However, the heavy influx of visitors can sometimes diminish local participation, creating a tension between preservation and commercialism.
ía de los Muertos
Día de los Muertos is celebrated on November 1st and 2nd. It honors deceased loved ones, showcasing vibrant altars and familial gatherings. The key feature here is the belief that spirits return to enjoy the offerings. This day is filled with colors, candles, and food, emphasizing the importance of family and remembrance.
This celebration offers a unique perspective on life and death, allowing families to cherish memories. Yet, the melding of traditions can cause confusion between indigenous and Catholic practices. Such cultural intersections must be thoughtfully addressed.
Traditional Cuisine
Traditional cuisine encapsulates the essence of Guatemalan culture. Food is a medium of expressing heritage and community values.
Staples of Guatemalan Food
Staples of Guatemalan food include corn, beans, and rice. These ingredients form the base of many meals. Their presence highlights indigenous agricultural practices that have endured for centuries. Simple yet nutritious, these staples support the daily diet of many Guatemalans.
Such staples are ideal for exploring Guatemala's dietary traditions. They encourage healthy eating habits, but reliance on these may limit dietary diversity. Understanding the nutritional aspects is significant.
Unique Dishes
Unique dishes in Guatemala include Pepian, a rich and spicy stew, and Kak'ik, a traditional turkey soup. Both delicacies showcase flavors rooted in indigenous cooking techniques. The preparation often involves family gatherings, fostering connections across generations.
These dishes represent more than mere food; they signify cultural pride. However, traditional meals may not always be accessible for everyone, often depending on regional resources. Discussing food brings attention to economic disparities as well.
By understanding cultural richness, we grasp the essence of Guatemalan identity—it is not only about the past, but also about shaping the future.
Biodiversity in Guatemala
Biodiversity is a crucial part of Guatemala's identity. It covers the variety of life forms here, from plants to animals. This diversity influences ecosystems, culture, and economy. Protecting biodiversity offers numerous advantages, such as maintaining ecological balance, supporting local economies and preserving cultural heritage. In a world facing environmental challenges, understanding and protecting this richness is essential.
Flora and Fauna
Endemic Species
Endemic species refer to plants and animals found only in a specific region. Guatemala is home to several endemic species, showcasing its unique biodiversity. These species have adapted specially to the local environment.
One key characteristic of endemic species in Guatemala is their role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. For instance, the Quetzal bird is both national symbol and an important part of the forests it inhabits. Their unique features make them crucial for seed dispersal and maintaining plant population.
However, these species face challenges like habitat loss. Protecting endemic species is vital for conservation efforts and maintaining biodiversity. The presence of these unique organisms adds notable value to the region, making it a focal point for ecological studies and conservation projects.
Protected Areas
Protected areas in Guatemala play a significant role in conserving biodiversity. They are designated regions that guard flora and fauna from human disturbances. These areas help preserve habitats, protecting many endemic and threatened species.
A notable aspect of protected areas is their contribution to the study of biodiversity. They serve as biological reserves, allowing scientists and researchers to observe ecosystems in their natural state. The unique feature of these areas is that they provide a safe space for many species to thrive, away from urbanization and deforestation.
While these areas have many advantages, they can also face challenges like illegal logging and poaching. Thus, maintaining and enforcing protections is crucial for preserving the biodiversity found in Guatemala.
Natural Habitats
Tropical Rainforests
Tropical rainforests in Guatemala represent one of the most biodiverse ecosystems globally. They are rich in plant and animal life, showcasing dense vegetation. These forests absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen, playing an important role in the global environment.


One key aspect of tropical rainforests is their diversity of species. Many animals and plants rely entirely on this ecosystem for survival. The rich variety enhances ecological stability by supporting food webs and interactions among species.
Nevertheless, the threats of deforestation and climate change put these ecosystems increasingly at risk. Recognizing the importance of tropical rainforests is essential for conservation efforts.
Cloud Forests
Cloud forests are another unique habitat found in Guatemala. They exist between lowland and highland areas, characterized by constant fog and high humidity. This environment supports a wide array of biological life and is home to numerous endemic species.
The key characteristic of cloud forests is their elevated moisture levels, which create unique ecosystems. They are essential for water retention and contribute to the water cycle. The high biodiversity found in cloud forests is also vital for scientific study and conservation.
Despite their importance, cloud forests face serious threats from agriculture and climate change. Protecting these areas is crucial to maintain their ecological balance and safeguard the unique species that inhabit them.
"Guatemala's biodiversity is not just about numbers; it's about the intricate connections between species and their environments."
Understanding and valuing biodiversity in Guatemala leads to greater awareness of conservation efforts and promotes sustainable practices among the local communities. Efforts to protect these ecosystems ultimately benefit both people and the earth.
Economic Aspects
Understanding the economic aspects of Guatemala is critical for a well-rounded view of its significance globally. Economic activities significantly influence daily life and culture. Examining these elements helps discover how economic growth is intertwined with the beautiful scenery, ancient history, and rich traditions of the country.
Key Industries
Agriculture
Agriculture plays a vital role in Guatemala's economy. It is one of the largest contributors to the nation's GDP. The country benefits from a favorable climate and fertile soil, allowing for the cultivation of a variety of crops.
Some main products include coffee, bananas, and sugar cane. Coffee, in particular, is a symbol of pride for Guatemala. It's well-known for its quality and flavor. The country's unique geographical conditions create perfect environments for these crops.
- Characteristics:
- Diverse crop production
- Significant employment opportunities
Agriculture supports thousands of families, making it not only beneficial economically but also socially. However, it also faces challenges, such as climate change, which can affect crop yields.
Tourism
Tourism is another key aspect of Guatemala's economic landscape. This industry brings many visitors who come to enjoy the archaeological sites, rich culture, and stunning nature. It provides jobs in various sectors, including hospitality and transportation. Visitors often seek experiences that highlight Guatemala’s history and traditions.
- Characteristics:
- Variety of attractions, from natural parks to Mayan ruins
- Boosts local businesses and crafts
Gaining international attention, tourism has the potential for growth. However, issues like sustainability and environmental degradation must be considered carefully. Because as the tourist numbers grow, the pressure on natural resources increases as well.
"Tourism enables communities to showcase their culture, but it must be managed to protect the heritage for future generations."
The balance between agriculture and tourism is crucial for Guatemala. Both industries run parallel to each other, showcasing the country's rich resources and possibilities.
Education and Environmental Awareness
Education plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of individuals and society. In Guatemala, this concept intertwines closely with environmental awareness. Understanding how to care for the environment begins at a young age. When children learn about the forests, rivers, and mountains around them, they develop respect for the natural world. This respect can lead to a desire to protect it.
The unique biodiversity of Guatemala provides a rich context for educational programs. Students can explore the significance of various ecosystems, like tropical rainforests and cloud forests. By incorporating local flora and fauna into the curriculum, students better appreciate these natural treasures. Moreover, environmental education often promotes critical thinking, enabling children to ponder the impact of human actions on the planet.
"Education is not preparation for life; education is life itself."
Environmental awareness contributes to a collective effort. When communities understand the importance of sustainability, they become proactive in protecting their environment. This not only has benefits for the ecosystem but also improves the quality of life for the people. For instance, clean water and healthy air are direct outcomes of a community that prioritizes environmental care.
Educational Initiatives
Several organizations focus on implementing educational initiatives in Guatemala. These programs aim to inform students about environmental issues and sustainable practices. Schools include lessons on conservation, focusing on local ecosystems. Interactive activities, such as field trips to national parks or nature reserves, help to bring these concepts to life. Young learners engage through hands-on experiences, fostering a deeper connection to their surroundings.
Local NGOs often collaborate with schools to offer workshops. These workshops cover various topics, from recycling to biodiversity conservation. By working together, they inspire a new generation of environmental stewards who understand the importance of their role in protecting nature.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts in Guatemala encompass various strategies aimed at preserving the environment. The government and non-profit organizations often team up to protect endangered species and restore damaged habitats. National parks, like Tikal National Park, serve as both a refuge for wildlife and a center for ecological education. Visitors to these parks learn about the importance of biodiversity and the steps necessary for preserving it.
Community-based conservation programs encourage local participation. Residents often benefit directly from protecting their resources. For example, by engaging in sustainable tourism, communities generate income while safeguarding their environment.
An essential aspect of these efforts is raising public awareness. Campaigns that highlight the importance of conserving natural resources can lead to positive changes in behavior. When families understand the impact of pollution or deforestation, they are more likely to participate in cleanup initiatives or tree-planting activities.
In summary, the combination of education and environmental awareness holds the power to transform Guatemala. Through educational initiatives and effective conservation strategies, individuals, communities, and ultimately the environment will thrive.







