Triceratops: Explore the Life of a Fascinating Dinosaur


Nature Topic Overview
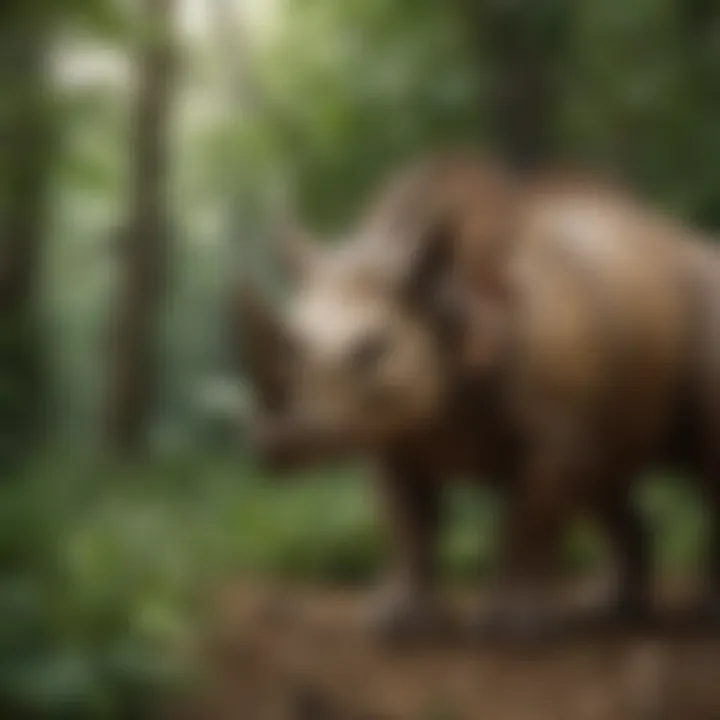
Imagine stepping back in time to a world where gigantic dinosaurs roamed the Earth. One of the most striking figures of this age was the Triceratops. This unique dinosaur stood out not only for its impressive size but also for its distinctive three horns and a large bony frill that guarded its neck. Picture a creature that could measure up to 30 feet long and weigh as much as a car!
Triceratops belonged to a group known as ceratopsians. It lived during the late Cretaceous period, around 68 to 66 million years ago – a time when the world was dominated by dinosaurs. It was mostly found in what is now North America, particularly in regions like Montana and Wyoming.
The name "Triceratops" itself means "three-horned face," and it is well-deserved. These majestic dinosaurs are fascinating to learn about because they were much more than just their horns and frill. Tracking their habits, understanding their diets, and uncovering their role in the environment provides a comprehensive glimpse into life millions of years ago.
Fun Facts and Trivia
Here are some cool facts that make the Triceratops even more fascinating for young minds:
- Social Creatures: Triceratops may have lived in groups, suggesting they were social animals. Imagine them wandering together in prehistoric grasslands!
- First Discoveries: The first Triceratops fossil was discovered in the year 1887. That's over 130 years ago!
- Strong Defense: Those three sturdy horns were likely used for defense against predators like the Tyrannosaurus rex. They could really pack a punch!
"Learning about the past helps us understand life today."
For a more engaging experience, young readers can color pictures of Triceratops or piece together puzzles featuring these mighty dinosaurs.
Wildlife Explorations
Triceratops was part of a wonderful family of creatures. Other species include Styracosaurus and Pentaceratops, both with their own unique features. Each of these dinosaurs had horns and frills, but they varied greatly in shape and size.
Their habitats were rich in diverse flora, supporting a variety of other wildlife. For instance, the environment included fern-filled forests and conifer trees, which provided ample vegetation to munch on. Curious kids can learn about these plants, such as Cycads, which were favorites among herbivorous dinosaurs.
To make it interactive, consider challenging young explorers with a quiz - "What dinosaur is bigger, the Triceratops or a modern-day elephant?" (Spoiler: It’s the Triceratops! The average elephant stands around 10-13 feet tall while a full-grown Triceratops could be about 10 feet tall).
Environmental Awareness
Understanding Triceratops also brings awareness to conservation efforts today. Just as these dinosaurs roamed their ecosystems, the same principle applies to us today. Protecting species and their habitats is crucial for maintaining the balance of our planet. Children can engage in simple activities like:
- Clean-Up Drives: Organizing a local clean-up can help protect wildlife in community parks.
- Nature Walks: Going on hikes and learning about local plants and animals can foster a love for the environment.
Encouraging children to respect nature and understand its importance can make a significant difference in how we cherish our planet.
DIY Nature Activities
To bring the world of Triceratops even closer, children can try out these fun hands-on activities:
- Dinosaur Fossil Dig: Create a small excavation site using sand and buried toy dinosaurs. Kids can dig out their own fossils, mimicking paleontologists in the field!
- Craft a Triceratops: Using cardboard and paints, children can create their own life-size Triceratops model. This not only enhances their understanding of its anatomy but also encourages creativity.
- Outdoor Adventure: Plan a family hike, spotting trees and plants similar to those during the dinosaur era. It’s a fantastic way to learn about the environment and how different it is today.
In summary, the story of Triceratops is not just about what they looked like or how they lived; it's about learning from these ancient creatures. By exploring their traits, understanding their role in the ecosystem, and fostering a sense of adventure in nature, we can nurture a generation that respects and understands the importance of our world.
Preamble to Triceratops
When you think of dinosaurs, Triceratops often pops up right away. This isn't just because of its unique look; it’s a rockstar among dinosaurs that fascinates both kids and adults alike. From its impressive horns to its large bony frill, Triceratops stands out as a symbol of the herbivorous giants that roamed the Earth millions of years ago.
This section sets the stage for understanding Triceratops, diving into what makes this dinosaur unique and why it’s worth our attention. We'll explore its physical features, the period it thrived in, and what it can teach us about the history of life on Earth. Learning about Triceratops isn’t just about memorizing facts; it’s about grabbing a glimpse of a vastly different world where these creatures were the rulers of their environment.
What is a Triceratops?
So, what exactly is a Triceratops? This dinosaur belongs to a group called ceratopsians, which means “horned faces.” It roamed the land during the late Cretaceous period, around 68 to 66 million years ago. Let's break it down even further.
Triceratops had a distinctive shape. It was large, reaching lengths of up to 30 feet and standing about 10 feet tall at its hips, roughly the size of a modern elephant. Its most notable features are the three prominent horns on its face, two above the eyes and one on the nose, these horns were not just for show. They probably were used for protection against predators, like the fearsome Tyrannosaurus rex.
The frill, a large bony structure at the back of its head, added extra protection for its neck. This feature also played a role in social interaction, possibly helping these dinosaurs recognize one another or communicate.
Period of Existence
Triceratops lived during a thrilling chapter of Earth's history called the late Cretaceous period. This period was marked by the flourishing of dinosaurs, when large land and sea reptiles thrived across the planet. The late Cretaceous was also a time of varied climates, where environments ranged from lush forests to open plains. This variety allowed many dinosaurs, including Triceratops, to find food and adapt in different ways.
Not only did a mini ecosystem form around these dinosaurs, but the late Cretaceous period also witnessed the rise of other well-known dinosaurs. It's like a big party with dinosaurs of different shapes and sizes, living side by side! Triceratops likely roamed in herds, which offered safety in numbers against predators.
Understanding the world during the late Cretaceous gives us perspective on how Triceratops not only survived but excelled in its niche. It’s a reminder of how interconnected life can be, with each creature playing its part in the storyline of our planet’s past.
Physical Characteristics
Understanding the physical characteristics of the Triceratops gives us a clearer picture of its adaptations and survival strategies in the environment it inhabited. These features not only define its appearance but also play essential roles in its survival, social interactions, and role within its ecosystem. Each aspect from the distinctive frill to the robust body structure is like a puzzle piece that helps us comprehend the life of this majestic dinosaur.
Distinctive Features
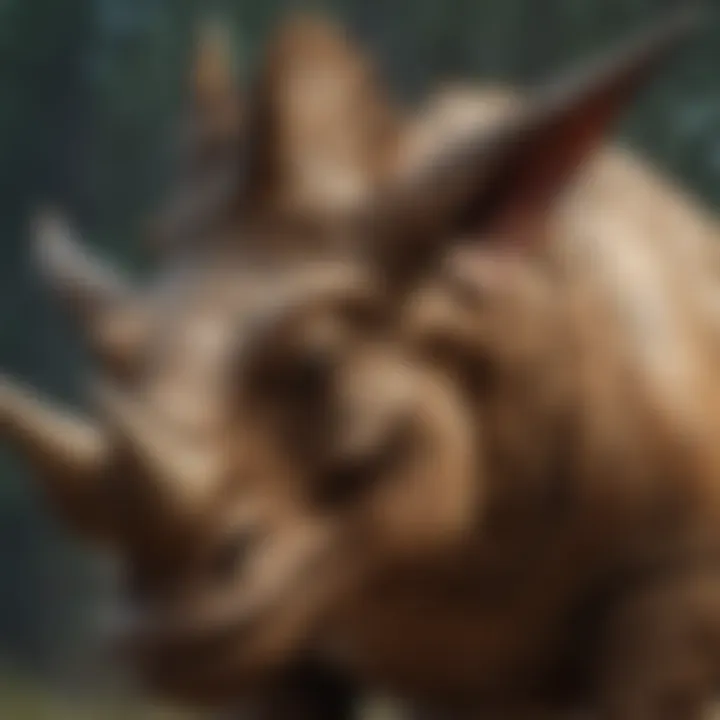


Frill
The frill of the Triceratops is quite notable. This large, bony structure at the back of its head serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it offers protection to the creature's neck from predator attacks, acting almost like a shield. Additionally, it likely played a role in mating displays, helping individuals attract partners by showcasing their health and vitality. The iridescent colors, possible presence of patterns, and even size variations could signify the strength of an individual.
The frill’s unique feature is that it is not just a solid piece; it has elaborate designs which likely could have helped in species recognition and individual identification. The large surface area might have also served to regulate body temperature, catching breezes and helping cool the massive creature down on hot days. In summary, the frill is not just a "look-at-me" aspect; it serves physical and social purposes that are significant in understanding the life of Triceratops.
Horns
Moving on to the horns, the Triceratops is probably most famous for its horned face. It possesses three distinct horns, with two longer ones above its eyes and a smaller nasal horn. These horns are believed to have been multipurpose tools in its life. Not just for defense against predators, but also possibly used in combat with other Triceratops during their mating season, or in competition for resources.
The robustness of the horns showcases an adaptation that speaks volumes about the Triceratops’s survival skills. They are made of bone, providing a sturdy, heavy-duty defense mechanism. The unique lead of these horns is that they could have also been involved in social interactions, signaling age or fitness to prospective mates. These factors make the horns an essential aspect of understanding Triceratops.
Body Structure
The body structure of the Triceratops is equally remarkable. Built like a tank, this dinosaur had a sturdy frame equipped for a herbivorous diet, capable of supporting its massive head and those formidable horns. The strong legs indicate that it was a powerhouse, able to move quickly when needed, despite its size. Furthermore, the body structure allows for efficient foraging in its habitat.
What stands out about Triceratops's body is its center of gravity. With a broad and robust build, it could maintain balance while grazing on low-leaved vegetation and shrubs. This characteristic is vital as it paints a picture of an animal perfectly adapted to its environment. All in all, the body structure encapsulates how Triceratops effectively thrived in a prehistoric landscape dotted with both food sources and potential threats.
Size and Weight
Size and weight are critical elements that further define what made the Triceratops an unforgettable dinosaur in the annals of prehistoric history. Understanding its scale provides insights into its lifestyle, its ecological niche, and even how other creatures responded to its presence.
Average Height
On average, a fully grown Triceratops stood about 10 feet tall at the hips. This impressive height offers perspective into how it interacted with its environment. The elevated stance allowed it to reach vegetation that other smaller herbivores would have struggled to access. Plus, its height undoubtedly aided in spotting potential danger from greater distances, giving it a fighting chance against predators.
The unique feature of this average height reinforces how it could thrive in various environments. Being taller may have also allowed Triceratops to have dominance over other herbivores in its territory, influencing its social standing in the ecosystem.
Length Measurements
In terms of length, Triceratops could stretch to approximately 26-30 feet overall. This length is significant in showcasing its massive bulk, which was not just for show. The longer body offered it stability and balance, crucial for a creature that might need to charge at predators or competitors. To fully grasp the scale of Triceratops in its habitat, considering its length primes the reader for appreciating its dinosaur neighbors.
The notable aspect of this length is its practical implications. A longer body shouldered an equally strong neck, which helped in foraging while allowing it to graze on a variety of plant life. This adaptability underlines why Triceratops was a formidable presence in its world.
Weight Comparison
When it comes to weight, fully grown Triceratops could tip the scales at around 12 tons. This enormous size made it one of the heaviest land animals of its time. A creature of such mass was not just for intimidation — in many ways, it was a testament to its evolutionary success. For young explorers, visualizing a creature that can weigh as much as three cars can evoke awe.
The unique feature of its heft is multifaceted; while it offers protection against predators, it also plays into its feeding behaviors. Heavier animals require copious amounts of plant matter to sustain them. Thus, Triceratops became a key player in its ecosystem, affecting plant life through its grazing habits. Understanding its weight compels readers to appreciate the balance of nature and the important role this dinosaur played within it.
"The Triceratops represents more than just a dinosaur; it stands as a testament to survival in a time filled with giants."
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding the habitat and distribution of Triceratops is essential, as it paints a fuller picture of how this remarkable dinosaur thrived during its time. Their habitat played a significant role in shaping their behavior, social structures, and diet. Knowing where they lived and the environments they adapted to can help us comprehend their needs and interactions with other species. This exploration leads us to imagine the landscapes of North America during the Late Cretaceous period, giving us a clearer view of their lives.
Geographical Range
North American Locations
The North American location of Triceratops fossils is quite fascinating. The majority of their remains have been found in what is now the western United States, especially in places like Wyoming, Colorado, and South Dakota. This region was swampy and had lush vegetation at that time. Such locales were ideal for nurturing the hefty herbivores like Triceratops. A key characteristic of these sites is the rich deposits of sediment, which often preserved the fossils exquisitely.
The unique feature here is the specific rock formations, such as the Hell Creek Formation, that give paleontologists clues about the climate and environment of the era. These conditions not only allowed Triceratops to exist but also influenced their herd behaviors and feeding practices. The drawbacks might include the challenges of finding remains, as conditions over millions of years altered the original settings quite a bit.
Associated Ecosystems
The associated ecosystems where Triceratops thrived were incredibly diverse. They lived alongside a variety of other dinosaurs and prehistoric life forms. This mingling is crucial to understanding their role in the ecosystem. A key characteristic of these ecosystems was the abundance of plant life. During the Late Cretaceous, ferns, cycads, and flowering plants offered a bountiful buffet for these creatures.
One unique feature of these ecosystems is their ability to support large herbivores without exhausting resources. The cyclical nature of plant growth ensured that Triceratops had enough foliage to consume. However, the competition with other dinosaurs could present challenges, as food sources might have turned sparse in some seasons. Regardless, these ecosystems painted a lively backdrop for the life of Triceratops.
Preferred Environment
Flora Composition
The flora composition in Triceratops' habitats mostly consisted of soft, leafy plants, which were perfect for their primarily herbivorous diet. They particularly favored ferns and cycads due to their abundance and nutritional value. This specific type of vegetation significantly contributed to Triceratops’ well-being, as the dinosaur required vast quantities of plant material to sustain its large body. A beneficial aspect of this flora was that it provided shelter from predators as well; the dense vegetation not only offered sustenance but also hid them from potential threats.
One unique feature to notice is how these plants adapted to the dino era, evolving alongside giants like Triceratops. They thrived in a warm, moist environment, which lent itself well to the growth of such foliage. However, a downside might have been periods of drought where resource availability would have waned, creating harsh conditions.
Climate Conditions


The climate conditions during the reign of Triceratops were generally warm and temperate, which favored the rich plant life that supported their diet. That's key! The steady climate allowed for consistent growth of vegetation. Triceratops thrived in environments that experienced wet and dry seasons, which ranged from lush green valleys to drier stretches. This variability would have encouraged the dinosaurs to migrate to where resources were abundant.
A unique aspect of the climate is how it influenced the behavior seen in social structures of Triceratops. Being social creatures, they likely adapted their herd movements based on seasonal changes to track food sources. Nevertheless, they may have faced challenges during extreme weather events like storms, impacting their living conditions and how they interacted with their environment.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Understanding the diet of Triceratops is crucial for grasping how this magnificent creature lived and thrived in its environment. As a herbivore, its feeding habits were closely linked to the ecosystem it inhabited, influencing both its health and survival. The effectiveness of Triceratops in finding food reflects its adaptation and highlights its role in the ancient food web.
Herbivorous Diet
Triceratops was primarily a herbivore, which means it dined on plants. The range of its diet was quite varied, including:
- Leafy greens: Triceratops munched on ferns, cycads, and conifers, which were abundant in its habitat.
- Shrubs and small trees: With its strong beak-like mouth, it could snap off thicker branches to access nutritious foliage.
- Low-lying vegetation: It also fed on softer plants close to the ground, making sure nutrients were always at hand.
This dinosaur's diet played a substantial role in shaping the vegetation of its time. By consuming large quantities of plants, Triceratops contributed to the growth and spread of certain species while controlling the growth of others. This balancing act likely had cascading effects on its ecosystem. As it foraged, it also helped seed dispersal, further promoting plant diversity.
Feeding Mechanisms
To accommodate its plant-based diet, Triceratops had evolved remarkable feeding mechanisms. These include:
- Beak-like Mouth: The front of its jaw resembled a beak, allowing for precise snipping of foliage. This adaptation was key for accessing different types of plants.
- Strong Teeth: Its teeth were flat, designed for grinding up tough plant material. This was essential for breaking down fibrous food, helping with easier digestion.
- Neck and Head Movements: The flexibility of its neck allowed Triceratops to reach a wide area of vegetation, maximizing its feeding efficiency by targeting multiple plant types.
"The structure of its mouth and teeth facilitated a varied diet, making it a true master of herbivory in the Late Cretaceous period."
Through these mechanisms, Triceratops was very well-equipped to thrive in its surroundings. This not only reflects the adaptability of the species but also points to the intricate relationship between diet and environment in prehistoric life. As we dive further into the legacy of this remarkable dinosaur, one can appreciate how its feeding habits played an essential role in ecological dynamics over millions of years.
Behavior and Social Structure
Understanding the behavior and social structure of Triceratops adds a fascinating layer to our knowledge of this iconic dinosaur. Behavior provides insight into how these creatures interacted not just with each other but also with their environment. For young minds exploring the life of Triceratops, grasping its social dynamics can spark curiosity about the primal instincts that guided their survival during the Cretaceous period.
Social Interaction
Herding Behavior
Herding behavior is a critical aspect of Triceratops' social life. By moving in groups, these dinosaurs could create a sense of security. There was strength in numbers, making it harder for predators like Tyrannosaurus rex to target any single individual. Being in a herd likely allowed them to raise young, share foraging spots, and protect one another against danger.
One key characteristic of this behavior is coordination. The ability to move together as a unit showcases intelligent social organization. Young explorers might find it interesting to know that such behavior can often be seen in modern animals, providing a direct link to contemporary wildlife and adding relevance to our understanding.
However, herding does come with some downsides. For example, being in a large group can make it more difficult to find food if resources become scarce. Still, the benefits of safety and societal bonding likely far outweighed the negatives in this dinosaur's prehistoric world.
Territoriality
Territoriality played an important role in the lives of Triceratops. While they often moved in herds, individual Triceratops would also stake out their areas. This behavior ensures access to food, mates, and safe nesting sites. The key characteristic of territoriality is the defensive strategies used to protect claimed territory. By standing their ground and using their impressive horns, Triceratops could discourage other dinosaurs from invading their space.
This aspect of their behavior is crucial for youngsters to understand. It emphasizes the need for resources and how competition shaped the lives of these ancient creatures. However, being territorial can be risky; it could lead to confrontations with others who are equally eager to claim the best patches of land.
Predator Defense Mechanisms
In the world of dinosaurs, defense mechanisms against predators were essential. Triceratops has developed several effective strategies to ensure survival against formidable threats.
Use of Horns
The use of horns is perhaps the most iconic feature associated with Triceratops. These weapons were not just for show; they were crucial in combat against predators. The arrangement and size of the horns could vary, but they generally served a similar purpose: to fend off attacks. When faced with danger, a Triceratops could charge at a predator. Their strong, powerful frames and these sharp appendages made them formidable foes.
In discussing this feature, it's clear why it is so beneficial. It showcases evolutionary advantages in terms of survival tactics and adaptation to their environment.
Behavioral Responses
Behavioral responses are another necessary component of how Triceratops defended themselves from predators. When sensing danger, their first instinct might have been to become alert, using their keen eyesight to spot threats. This would involve quick reactions, such as fleeing to join their herd or taking a defensive stance.
This characteristic is significant as it relates to instinctual behavior that persists in the animal kingdom today. The ability to rapidly adapt to threats shows a level of intelligence and survival skill that is both fascinating and essential. However, such responses could sometimes fail if the threat was unexpected, leading to potential loss or injury, underscoring the harsh realities of life in the wild.
In sum, Triceratops' behavior, from social interactions to predator defense, adds richness to our understanding of their existence. It marks a critical point in appreciating the complexity of these dinosaurs, making them much more than mere fossils trapped in time.
Fossil Record and Discoveries
Fossils are like time capsules from the past, providing a glimpse into the lives of creatures that roamed the Earth millions of years ago. The fossil record of Triceratops is especially rich, offering crucial insights into its biology and behavior. Understanding these discoveries is pivotal, as they not only shed light on Triceratops itself but also help unravel the ecology of the late Cretaceous period.
Major Fossil Sites
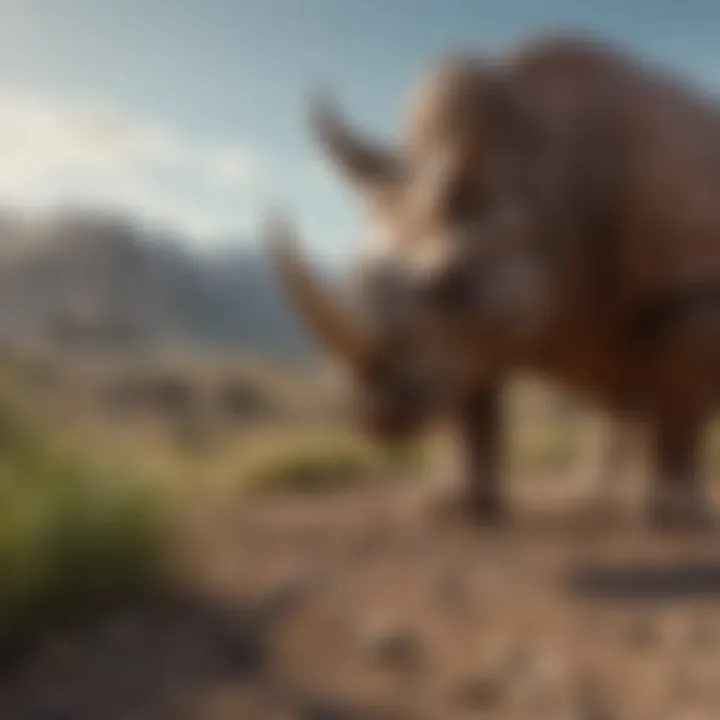


Triceratops fossils have been unearthed in various locations, with some sites standing out due to their historical significance. Notably, the Hell Creek Formation in Montana has produced numerous Triceratops remains. This area is well-known among scientists for its wealth of dinosaur fossils, revealing a vibrant ecosystem that thrived during the late Cretaceous. The diversity of fossils found here can tell researchers about the different species that coexisted in this time, such as Tyrannosaurus rex and Ankylosaurus.
Another notable site is the Lance Formation in Wyoming, where Triceratops bones have been extensively studied. This site has also produced nearly complete skeletons, helping paleontologists piece together the anatomy and lifestyle of these remarkable dinosaurs. Such fossil-rich sites are invaluable in constructing the narrative of the timeframes when these giants walked the earth, making it easier to understand their evolution and adaptations.
Scientific Discoveries
Important Excavations
Excavating dinosaur fossils is like piecing together a gigantic puzzle. One of the most significant excavations was at the famous Bone Cabin Quarry in Wyoming. This site provided a treasure trove of Triceratops remains, including skulls, limbs, and frills. Paleontologists working in this quarry unearthed many unique fossils, each providing clues to the dinosaur's life.
These excavations contribute substantially to our comprehension of Triceratops. A key characteristic of these sites is that they not only yield bones, but also other geological information, like the type of soil and sediment. This gives scientists context about the climate, environment, and potential challenges these creatures faced. However, excavating fossils can be tricky. Bad weather or difficult terrain can hinder the work, making it a slow process.
Fossil Interpretation
Interpreting fossils requires a keen eye and a deep understanding of paleobiology. Researchers examine the shape, size, and markings of bones to uncover behaviors and lifestyles of Triceratops. A prominent aspect of fossil interpretation is comparing new finds to well-studied specimens. For example, through various techniques, experts have determined that Triceratops likely had a social structure, perhaps living in groups for protection.
Fossil interpretation allows scientists to perform a bit of detective work, piecing together how these dinosaurs interacted with their surroundings. One unique feature of this process is using advanced technology like CT scans. These tools help visualize internal structures without damaging delicate fossils. Yet, this approach can be costly and requires expert handling, marking a delicate balance between technology and traditional methods.
Cultural Impact and Representation
The cultural impact of Triceratops is quite profound, reflecting not only our fascination with dinosaurs but also how they inspire art, media, and education. This remarkable dinosaur has carved its niche in popular culture, serving as a symbol of prehistoric life. It's important to understand how various aspects of society engage with Triceratops, shaping both our perception of these creatures and our scientific understanding of the past.
In Popular Media
Movies
Movies have played a major role in bringing Triceratops to life for audiences of all ages. Films such as Jurassic Park introduced this dinosaur as a strong and brave character, appealing to both children and adults. The portrayal of Triceratops displays its formidable horns and massive stature, captivating viewers and igniting curious minds. These films provide an entertaining yet informative glimpse into the past, igniting imaginative thoughts and fostering an interest in dinosaurs.
The unique aspect of these movies is their ability to blend entertainment with a bit of science. However, they can sometimes take creative liberties, leaving out the nuances of real-life behavior and habitat. This can mislead viewers, making them think that these representations are completely accurate.
Books
Books about Triceratops serve as valuable educational tools, providing in-depth knowledge about its life and environment. Many children's books illustrate these dinosaurs with vivid images, making learning fun and engaging. Titles like National Geographic Kids’ Dinosaurs open a window to the past, offering facts and stories that fuel a child's imagination.
A key characteristic of these books is their ability to simplify complex scientific ideas into digestible information for younger audiences. This approach makes them a wonderful resource for parents and educators. However, some books may overlook intricate details, leading to gaps in understanding regarding the complexities of dinosaur life.
Symbolic Representation
Interpretations in Art
Triceratops is not just a creature of the past; it's a symbol in many cultures. In art, Triceratops is often depicted reflecting themes such as strength and resilience. Artists use this dinosaur to convey stories or emotions, allowing its image to speak volumes about our relationship with nature and history.
This artistic use emphasizes the need to remember and learn from our past. While paintings and sculptures can vary in accuracy, they possess a unique ability to evoke feelings and thoughts regarding prehistoric times, helping audiences to appreciate what was lost and what can still be learned.
Scientific Education
In the realm of education, Triceratops figures prominently. It becomes a gateway for teaching children about evolution, paleontology, and earth sciences. By incorporating this dinosaur into curricula, educators can spark a passion for science in young learners. The engaging stories about Triceratops encourage students to explore and ask questions, promoting a deeper understanding of the natural world.
The importance of scientific education lies in its ability to foster critical thinking and curiosity. Nonetheless, it's critical to balance excitement with accurate information to prevent misconceptions about prehistoric life.
Understanding how we've internalized Triceratops changes our perspective about these magnificent creatures, making them more than just ancient beings; they become part of our ongoing journey of discovery and knowledge.
Overall, the cultural impact of Triceratops shapes both individual and collective identities concerning the natural world, reinforcing its relevance in today's society.
The End
Drawing together the colorful threads of Triceratops’ story, we see how this spectacular dinosaur leaves behind a legacy that transcends its extinction. Understanding Triceratops provides a window into our planet’s distant past, shedding light on the ecosystems of the Late Cretaceous period. The way it stood firm with its majestic frill and impressive horns tells us about the challenges it faced and the strategies it crafted to survive. It teaches young explorers about resilience, adaptation, and the delicate balance of nature.
The Legacy of Triceratops
The cultural significance of Triceratops goes beyond its physical form. It has captured the imagination of many, becoming a favorite subject in films and literature. Young minds find inspiration in this creature’s tough demeanor and magnificent appearance. As a symbol of strength and adaptability, Triceratops encourages children to learn more about prehistoric life and the importance of conservation in today's world.
Key Points About Its Legacy:
- Triceratops frequently appears in animated movies, captivating younger audiences.
- It serves as a powerful reminder of the diversity and beauty of Earth's history.
- Museums display Triceratops fossils, stimulating curiosity about fossils and paleontology in children.
Continued Research
Scientific examination of Triceratops is ongoing and dynamic. New discoveries illuminate previously unknown aspects of this iconic dinosaur. Paleontologists tirelessly work to piece together the puzzle of its life, such as its behavior, climate adaptability, and evolution. Through advanced techniques like 3D imaging and stable isotope analysis, researchers can uncover facts that reshape our understanding of Triceratops.
Aspects of Ongoing Research:
- Excavation in various North American sites continues to yield valuable fossils.
- Comparisons with closely related species lead to richer insights about their social dynamics.
- Analysis of fossilized remains offers clues about their diet and habitat preferences.
"Every fossil tells a story; through them, we learn lessons about survival that echo through time."